VMware Horizon Cloud Service Next-Gen – The Automation Series – Chapter 5 – Site
This blog post is part of the VMware Horizon Cloud Service Next-Gen – The Automation Series, a series of blog posts that describes the possibilities and use of the VMware Horizon Cloud Service Next-Gen APIs.
In this chapter we will add, get and delete a site configuration. We will use PowerShell to execute the requests.
The original VMware documentation for site operations can be found here.
Create
We will start by creating a new site configuration. For this we will use the following information:
| HTTP Method | POST | |
| URI | https://cloud.vmwarehorizon.com/portal/v2/sites | |
| Content-Type | application/json | Header |
| Authorization | Bearer <Access token> | Header |
| orgId | Organization ID | Body |
| name | Any name for the site | Body |
| description | Any description for the site | Body |
With this information we will now construct the lines of code in PowerShell to add the site configuration.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
$Header = @{ "Content-Type" = "application/json"; "Authorization" = "Bearer " + $AccessToken } $Body = @{ "orgId" = "x1xxx1111-x111-1111-xx11-111111x11xx1"; "name" = "site-name"; "description" = "site description"; } Invoke-RestMethod -Uri https://cloud.vmwarehorizon.com/portal/v2/sites -Method Post -Headers $Header -Body ($Body | ConvertTo-Json) |
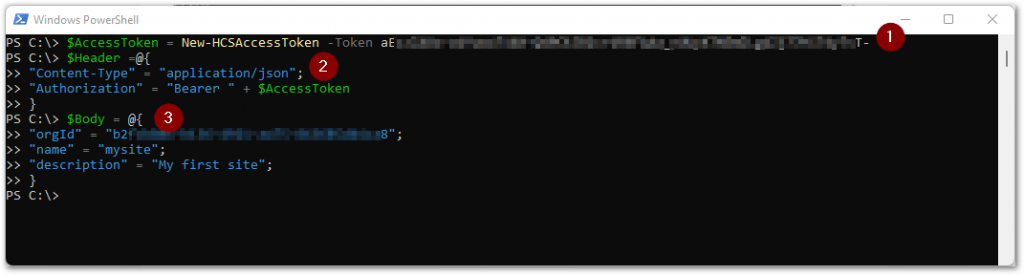
(1) We create the access token from the API token using the New-HCSAccessToken function we described in chapter 2. We put this value in the $AccessToken variable, which we will use in the following step.
(2) We then construct the $Header array, where we specify the expected Content-Type to be received by the URI, which is application/json. And we specify the type of authorization using the Bearer type with the access token from the variable $AccessToken.
(3) After this we construct the $Body array with all the items that define the site configuration to be added to the Horizon Cloud Services.
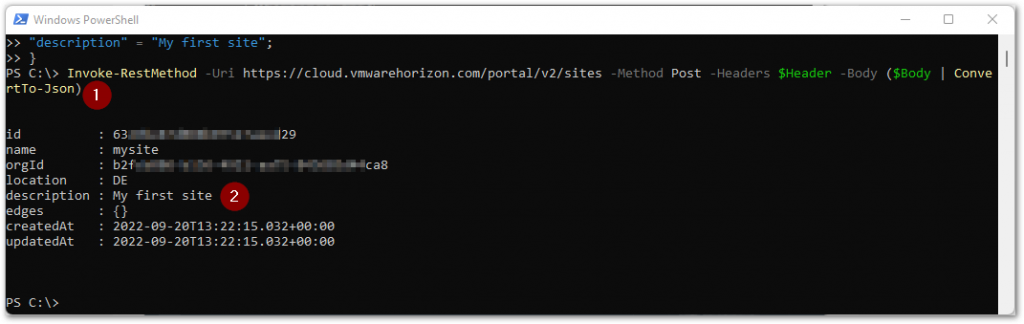
Now that we have both the Header and Body information in place, it’s time to execute the command to add the site configuration (1). Once executed, the output with what has been configured will be displayed (2).
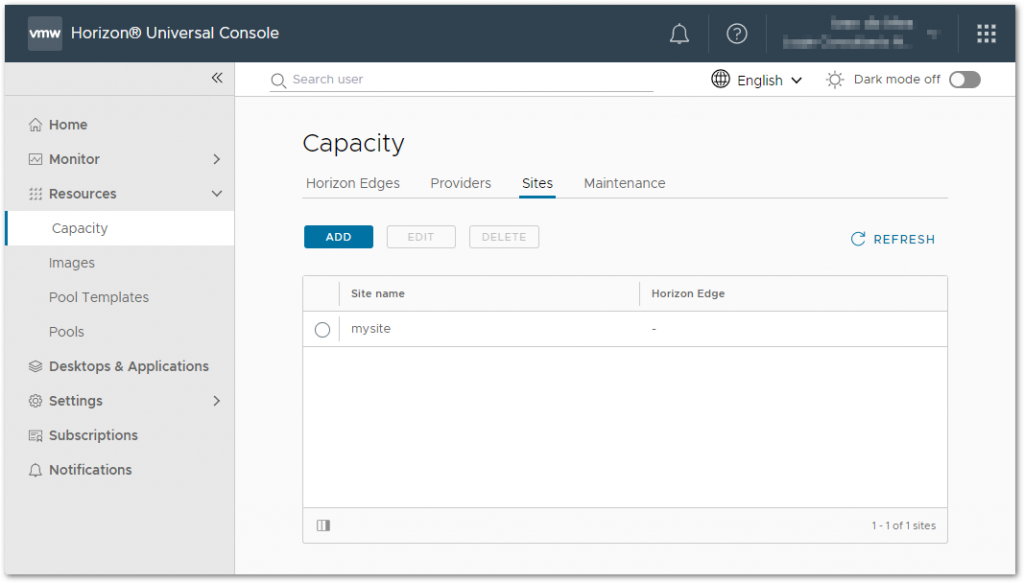
When we look in the Horizon Universal Console, we see that the site configuration is added.
Get
To retrieve the site configuration(s), we will use the following information:
| HTTP Method | GET | |
| URI | https://cloud.vmwarehorizon.com/portal/v2/sites | |
| Content-Type | application/json | Header |
| Authorization | Bearer <Access token> | Header |
With this information we will now construct the lines of code in PowerShell to retrieve the site configuration(s).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
$Header = @{ "Content-Type" = "application/json"; "Authorization" = "Bearer " + $AccessToken } Invoke-RestMethod -Uri https://cloud.vmwarehorizon.com/portal/v2/sites -Method Get -Headers $Header |
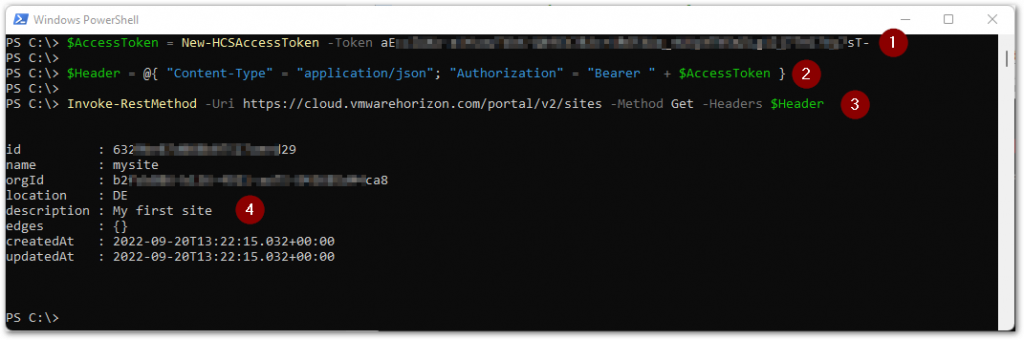
(1) We create the access token from the API token again using the New-HCSAccessToken function, and put this value in the $AccessToken variable, which we will use in the following step.
(2) We construct the $Header array, where we specify the expected Content-Type to be received by the URI, which is application/json. And we specify the type of authorization using the Bearer type with the access token from the variable $AccessToken.
(3) We execute the command to retrieve the site configuration(s).
(4) Once executed, the output with what has been configured will be displayed.
Delete
To delete a site configuration, we will use the following information:
| HTTP Method | DELETE | |
| URI | https://cloud.vmwarehorizon.com/portal/v2/sites/<site record ID> | |
| Content-Type | application/json | Header |
| Authorization | Bearer <Access token> | Header |
| id | Id for the site configuration | URI |
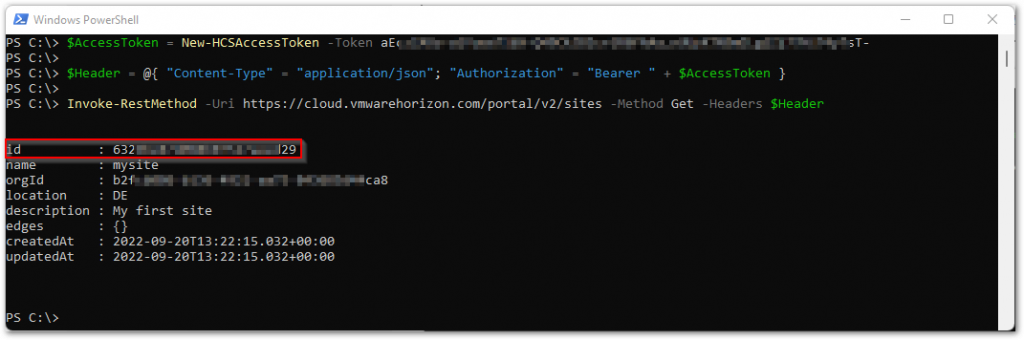
You can lookup the required site record ID using the steps from the Get paragraph. Look for the id value in the output.
With this information we will now construct the lines of code in PowerShell to delete the site configuration.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
$Header = @{ "Content-Type" = "application/json"; "Authorization" = "Bearer " + $AccessToken } Invoke-RestMethod -Uri https://cloud.vmwarehorizon.com/portal/v2/sites/<site record ID> -Method Delete -Headers $Header |
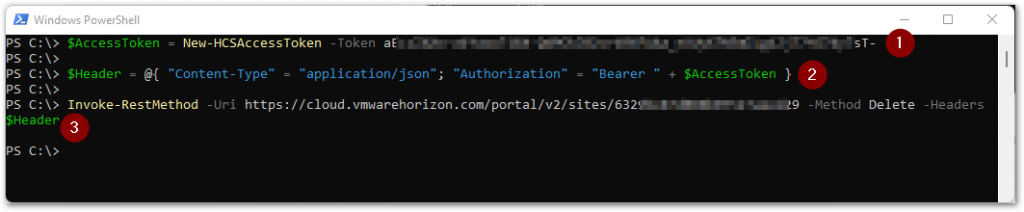
(1) We create the access token from the API token again using the New-HCSAccessToken function, and put this value in the $AccessToken variable, which we will use in the following step.
(2) We construct the $Header array, where we specify the expected Content-Type to be received by the URI, which is application/json. And we specify the type of authorization using the Bearer type with the access token from the variable $AccessToken.
(3) We execute the command to delete the site configuration. No output with what has been deleted will be displayed.
PowerShell Functions Examples
| The scripts below serve as examples. You may change the scripts to your own needs or standards, like error handling, securing password strings and things like that. |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
Function New-HCSSiteConfig { [CmdletBinding()] param ( [Parameter(Mandatory=$True)] [string]$AccessToken, [Parameter(Mandatory=$False)] [string]$Uri, [Parameter(Mandatory=$True)] [string]$OrganizationId, [Parameter(Mandatory=$True)] [string]$Name, [Parameter(Mandatory=$False)] [string]$Description ) If (!($Uri)) { $Uri = "https://cloud.vmwarehorizon.com/portal/v2/sites" } $Header = @{ "Content-Type" = "application/json"; "Authorization" = "Bearer " + $AccessToken } $Body = @{ "name" = "$Name"; "description" = "$Description"; "orgId" = "$OrganizationId" } Invoke-RestMethod -Uri "$Uri" -Method Post -Headers $Header -Body ($Body | ConvertTo-Json) -UseBasicParsing } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
Function Get-HCSSiteConfig { [CmdletBinding()] param ( [Parameter(Mandatory=$True)] [string]$AccessToken, [Parameter(Mandatory=$False)] [string]$Uri, [Parameter(Mandatory=$False)] [string]$Name ) If (!($Uri)) { $Uri = "https://cloud.vmwarehorizon.com/portal/v2/sites" } $Header = @{ "Content-Type" = "application/json"; "Authorization" = "Bearer " + $AccessToken } If (!($Name)) { Invoke-RestMethod -Uri "$Uri" -Method Get -Headers $Header -UseBasicParsing } Else { ForEach ($_ in (Invoke-RestMethod -Uri "$Uri" -Method Get -Headers $Header -UseBasicParsing)) { If ($_.name -eq "$Name") { Write-Output $_ $NameFound = $True } } If ($NameFound -ne $True) { Write-Warning "Name not found." } } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
Function Remove-HCSSiteConfig { [CmdletBinding()] param ( [Parameter(Mandatory=$True)] [string]$AccessToken, [Parameter(Mandatory=$False)] [string]$Uri, [Parameter(Mandatory=$True)] [string]$Id ) If (!($Uri)) { $Uri = "https://cloud.vmwarehorizon.com/portal/v2/sites/" + $Id } $Header = @{ "Content-Type" = "application/json"; "Authorization" = "Bearer " + $AccessToken } Invoke-RestMethod -Uri "$Uri" -Method Delete -Headers $Header -UseBasicParsing } |
I hope this chapter was informative and that you enjoyed reading.
Next up is provider instance configuration.




